Spectacular What Does Standard Deviation Mean In Normal Distribution

Low standard deviation means data are clustered around the mean and high standard deviation indicates data are more spread out.
What does standard deviation mean in normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is centered at zero and the degree to which a given measurement deviates from the mean is given by the standard deviation. Together with the mean standard deviation can also indicate percentiles for a normally distributed population. The following plot shows a.
Standard deviation 4. Examine the table and note that a Z score of 00 lists a probability of 050 or 50 and a Z score of 1 meaning one standard deviation above. Where X is a score from the original normal distribution m is the mean of the original normal distribution and s is the standard deviation of original normal distribution.
Standard deviation and normal distribution. Recall that for a random variable X Fx PX x. A standard deviation close to zero indicates that data points are close to the mean whereas a high or low standard deviation indicates data points are respectively above or below.
And you mention observations in the same sentence as mean and standard deviation which makes me wonder whether or not you mean estimates of both mean and standard deviation. 95 lie within two. If Z 0 X the mean ie.
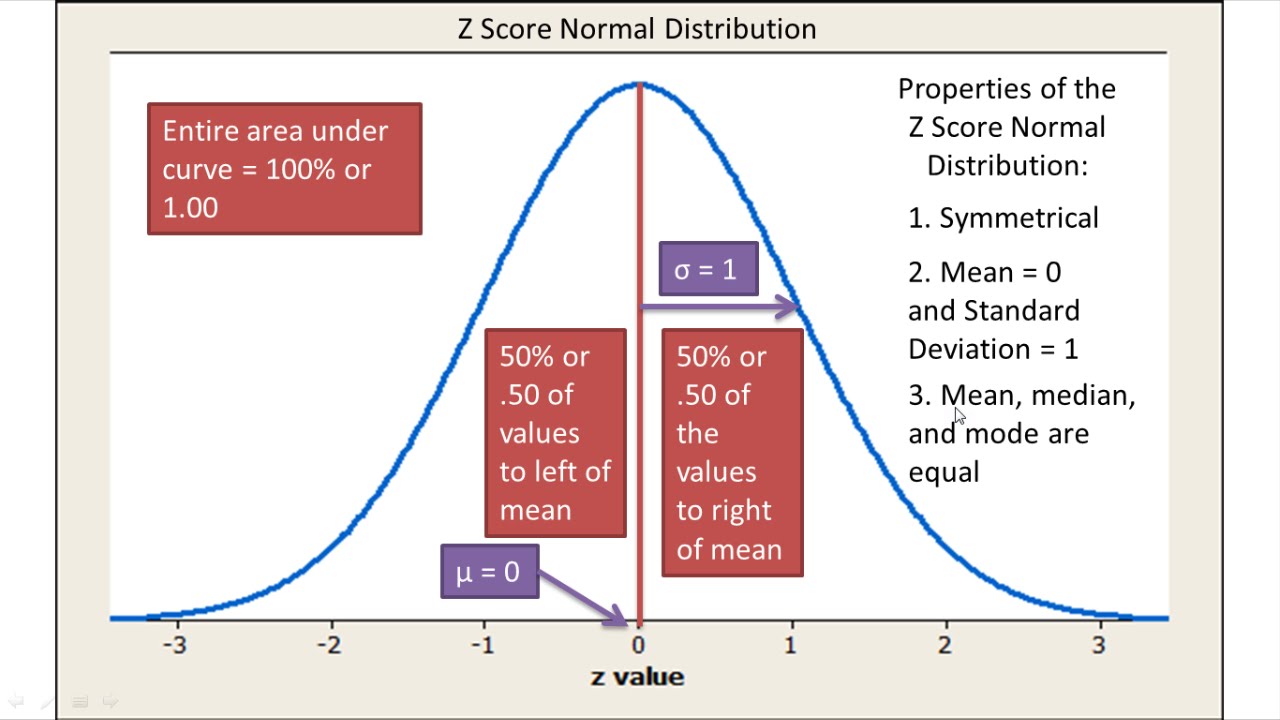
Normal Distribution - Change mean and standard deviation. For example the normal distribution N 0 1 is called the standard normal distribution and it has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
It shows how much variation or dispersion there is from the average mean or expected value. The diagram below is a standard normal distribution and the location of z-value is indicated on the horizontal axis. For the standard normal distribution 68 of the observations lie within 1 standard deviation of the mean.